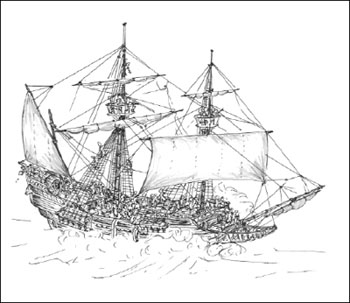
 The Galleon
The Galleon
Lady Fríða in hárfagra
A galleon was a large, multi-decked sailing ship used primarily by European states from the 16th to 18th centuries. Whether used for war or commerce, they were generally armed with the demi-culverin type of cannon. The galleon was an ocean going ship which evolved from the carrack. A lowering of the forecastle and elongation of the hull gave galleons an unprecedented level of stability in the water, and reduced wind resistance at the front, leading to a faster, more maneuverable vessel. The galleon differed from the older types primarily by being longer, lower and narrower, with a square tuck stern instead of a round tuck, and by having a snout or head projecting forward from the bows below the level of the forecastle.
The galleon was powered entirely by wind, using sails carried on three or four masts, with a lateen sail continuing to be used on the last (usually third and fourth) masts. They were used in both military and trade applications. They were the driving force behind much 15th and 16th century exploration. In fact, galleons were so versatile that a single vessel may have been refitted for wartime and peacetime roles several times during its lifespan.